Mass transfer and mass transport are associated with processes such as diffusion and convection, adsorption and separation as well as mass transfer and mass transfer (e.g. through porous media).
Examples:
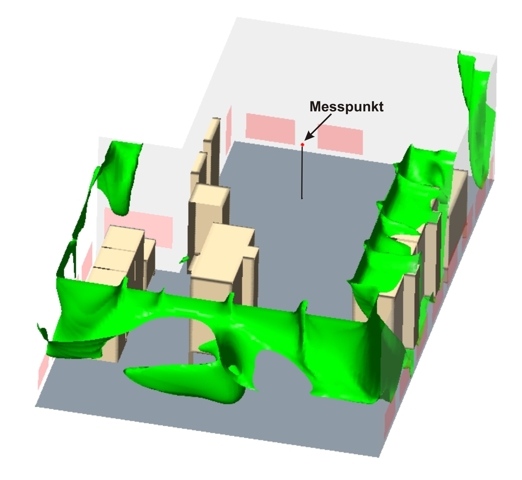
| Wash-out processes of substances in flow-through systems and devices (recovery test of clean rooms, smoke propagation / smoke removal from buildings) |
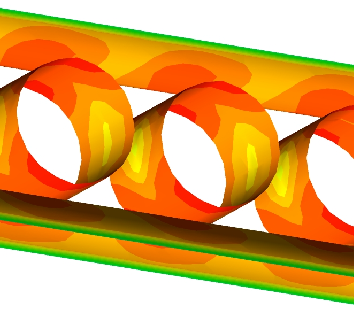
| Mass transfer in multiphase systems including chemical and/or biological reactions (fermenters) |
| Mass transfer from coated walls and packed beds (adsorbers) |
| Selection and filtering of substances (dust filters, gas separators) |
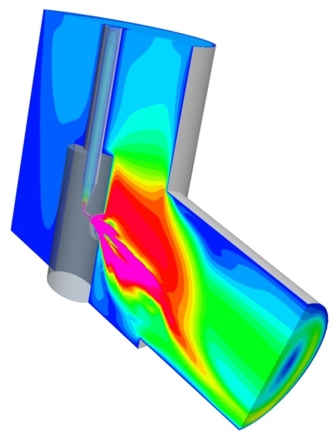
| Mass transfer through selective membranes (dialyzer and oxygenator) |
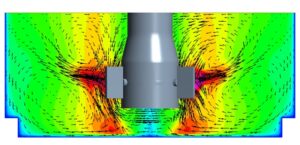
| Rotational separation (blood cell separator) |
| Media supply in cell culture systems (bioreactor) |
The analysis of these combined flow and mass transport systems with numerical simulation opens up the possibility of identifying detailed relationships, analyzing, differentiating and controlling influencing parameters, and impressively visualizing these processes.
Especially in biomedicine and medical engineering, one finds manifold processes of transport and exchange of different substances and materials. This concerns both natural organs or organ systems as well as devices that take over organ functions, such as the dialyzer. In these systems, it is usually difficult to visualize the internal distribution of the substances of interest in three dimensions or to recapitulate processes. Virtual methods, such as flow simulation, often offer the only possibility of understanding internal system processes and interrelationships. They are therefore an ideal starting point for effective optimization of artificial organs, for example.